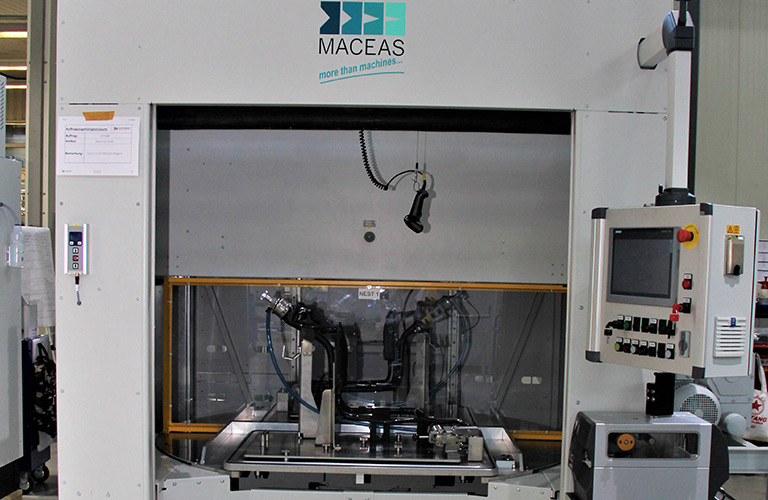
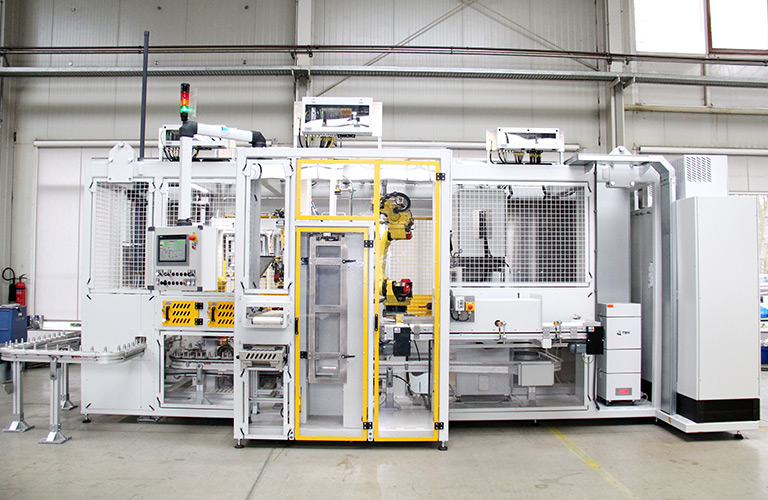
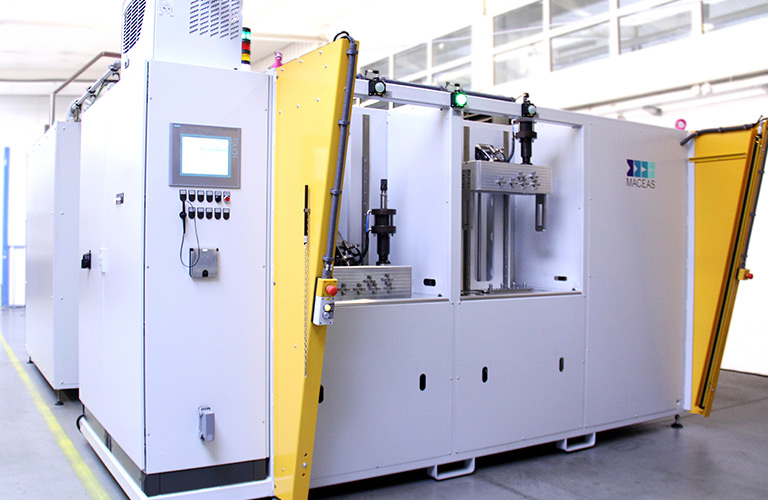
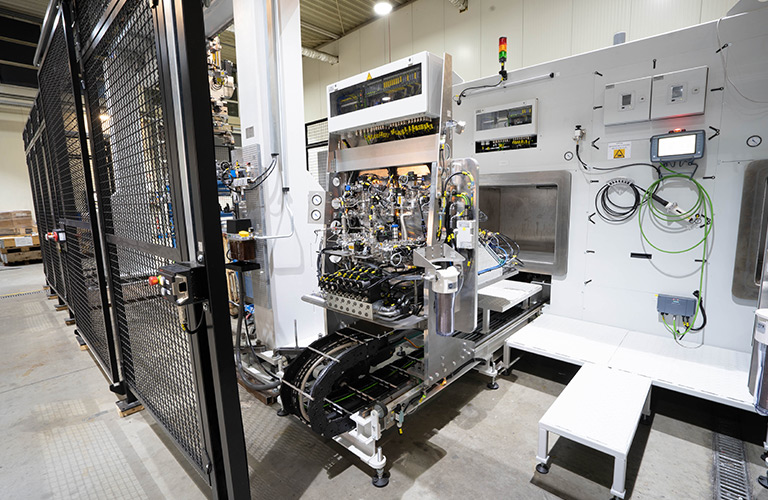
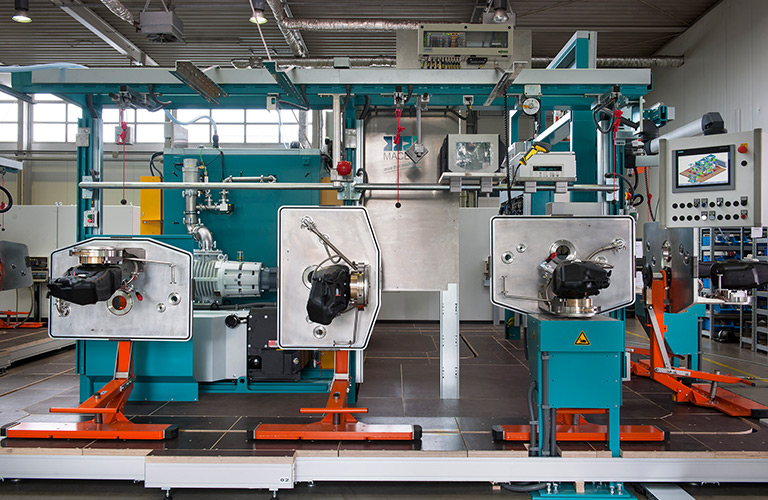
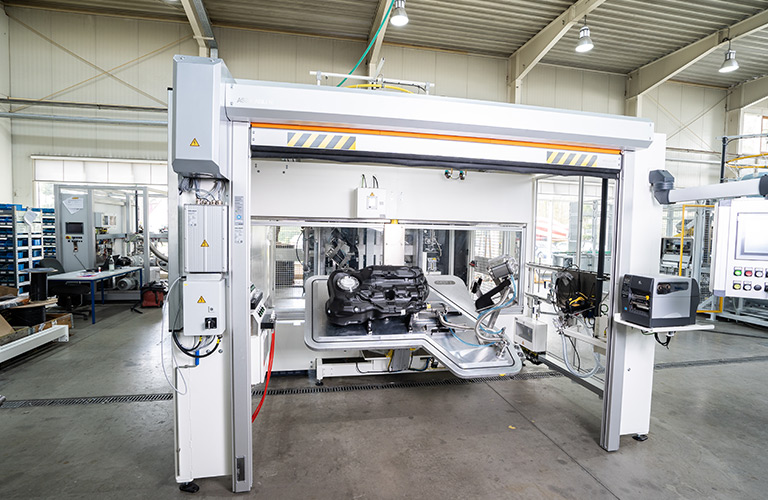
Reliably detect and localize leaks with a helium leak tester
Helium leak test systems were first used in 1942 as part of the so-called Manhattan Project. This was the birth of helium leak test. Today, helium leak testers are among the most established and accurate methods of leak testing in series production and in the laboratory. In addition to helium leak testing in a vacuum, which requires a high vacuum in the mass spectrometer, helium leak testing under atmosphere using helium sensors is now also used.
| Helium leak test in a vacuum | |
|---|---|
| Detection limit of a mass spectrometer: | 10–12 mbar ⋅ l/s |
| Working range leak testing system: | 10−3 – 10−7 mbar ⋅ l/s |
| Helium leak test under atmosphere | |
|---|---|
| Detection limit of the sensor: | 10–6 mbar ⋅ l/s |
| Working range leak testing system: | 10−2 – 10−4 mbar ⋅ l/s |
Both leak tests can be fully automated. An automated leak detection system can either be fully automated by means of robot handling or the parts handling is carried out manually by the worker. In both cases, the leak test is always automated.
Your benefits at a glance:
- Objective leak test in a vacuum and under atmosphere
- Quick and reliable leak detection
- Independent from influencing factors
- Single or multi-chamber testing system
- Fully automated system with robot handling
- No parts drying required
- Helium recovery system (optional)
- Article recording for other product variants (on request)
- Cycle time reduction through additional test chamber (optional)
Areas of application
Helium leak test for fuel cell plates
A main part of the fuel cell are the bipolar plates. It is very important for the process that the bipolar plates are leak free and no gas can pass the intended process because of leakages.
We have developed a helium leak test to check the plates. This device is able – with the specific tooling – to test single plates as well as bipolar plates.
Learn more!
Further information on helium leak testing
Helium leak test
There are two different methods of helium leak testing. On the one hand the helium leak test under vacuum and on the other hand the helium leak test in the atmosphere. While the detection of the helium gas flowing out of the leak with a mass spectrometer always requires a high vacuum in the mass spectrometer (p <10-4 mbar), helium sensors are now also available that no longer require a vacuum. However, much smaller amounts of helium can be detected with the mass spectrometer than is the case with other sensors.
Helium leak test under vacuum
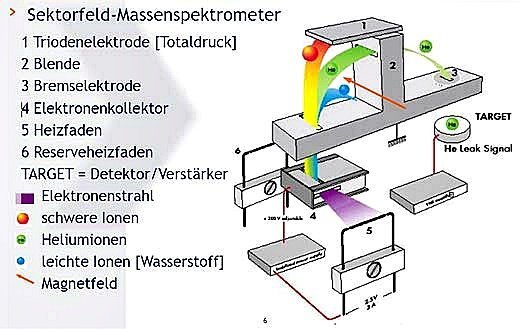
A mass spectrometer is required as a sensor for this method. The helium atoms are ionized with the help of an electron beam. The now electrically charged particles are directed onto a circular path in a magnetic field. The radius of the circular path depends on the mass of the particles. Only particles of a certain mass get through the slit in the diaphragm. These then generate an electrical current at the detector.
Measuring principle – test system / device
The vacuum test chamber and test part are evacuated. Then the test piece is exposed to helium or a He mixture. The previously existing vacuum in the test part ensures that the test gas is evenly distributed. After a certain vacuum has been reached in the test chamber, the mass spectrometer is switched on and the measurement is carried out. With a sniffer probe, the leakage can then possibly be localized in the atmosphere. Since only larger leaks can be detected with the sniffer probe, it may well happen that no leak is found. An alternative to locating the leak is to check it in a water bath.
Helium leak test under atmosphere
Measuring principle – WiseTM sensor
With the help of a maintenance-free helium sensor (e.g. T-GuardTM), an increasing helium concentration can be measured in a test chamber even at atmospheric pressure. The actual sensor consists of a quartz membrane that is only permeable to helium and a permanently evacuated glass tube (see tube television), as well as an anode ring and a cathode plate. At a concentration of 5ppm helium, a current of 2-10-10A flows.
Measuring principle – test system / device
With the help of fans or a circulation, in the event of a leak (helium flows into the chamber), the most homogeneous possible distribution in the chamber is created. This is necessary because otherwise leaks at different points would result in very different readings.